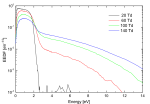
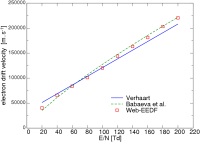
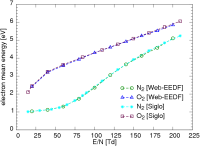
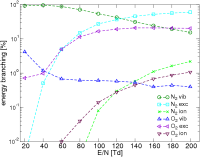
Results
Publications:
|
Janda M., Martišovitš V., Morvová M., Machala Z., Hensel K.: Monte Carlo Simulations of Electron Dynamics in N2/CO2 Mixtures, accepted in Eur. Phys. J. D (2007)
abstract |
| Janda M.: The Study Of Plasma Induced Chemistry In Gaseous Mixture N2-CO2-H2O, Thesis, Comenius University Bratislava, Universität Innsbruck (2006) |
| Abstract: Chemistry induced by atmospheric pressure DC discharges burning to the water surface in N2-CO2-H2O mixture was studied. For this purpose, positive polarity electrical discharges of transition type named according to their properties 'Spontaneously Pulsing Transition Discharge' and 'High Pressure Glow Discharge' were applied. Studied gaseous mixture represents a model prebiotic atmosphere of the Earth and simplified flue gas from the stoichiometric combustion of natural gas. The aim was the formation of organic species, especially amino acids, and the CO2 abatement. Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy was used to analyze gas samples, and solid deposits from electrodes. Liquid samples were analyzed by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Proton-Transfer-Reaction Mass Spectrometry. For better understanding of induced plasma chemistry, two computational methods were also applied: Monte Carlo simulations of electron dynamics in order to calculate rate coefficients of various electron impact reactions in studied mixtures, and Quantum Mechanics calculations of thermodynamic parameters of species and reactions which could be involved in the synthesis of detected species. The most remarkable changes in the chemical composition of the treated gas are the removal of CO2 and the production of CO. The concentration of CO increases logarithmically with increasing input energy density (Ed) and growing initial concentration of CO2. The highest achieved concentration of CO was 4.0 ± 0.5 vol.% (Ed ≈ 700 J/l, 100 vol. % of CO2 in the input gas). The energy required for the removal of one CO2 molecule (EdeCO2) decreases exponentially with growing concentration of CO2 and it remains almost equal, 60 ±10 eV, for concentration of CO2 above 30 vol.%. This value is still very high and CO is more harmful than CO2, this technology is therefore not suitable for CO2 abatement from flue gas. It might be used in special cases, for example for the production of syn-gas (CO/H2) or more valuable organic compounds by the treatment of pyrolysis gases or exhaust gases enriched by CH4. In this case would be the production of CO desired. The production of CO is most probably crucial also for the synthesis of organic species, since reactions of the CO with some reactive species generated in plasma, e.g. H, N, N2*) are most probably the starting point in the synthesis of organic compounds. The synthesis of organic species was confirmed by all performed analysis of solid and liquid samples. The most important for the theory of the origins of life was the detection of Serine, Histidine, Glycine, and Prolyne by HPLC. The presence of two more amino acids, Alanine and Valine, is also very probable. It is very important that the synthesis of amino acids is possible even in inorganic N2-H2O-CO2 atmosphere. The enrichment of this atmosphere by small amount of hydrocarbons would only facilitate the chemical evolution of life. |
|
Janda M., Hensel K., Martišovitš V., Morvová M.: Theoretical Study of Influence of H2O on Parameters of Low-Temperature Plasmas in Humid Mixtures, Czech. J. Phys., 56, B774-B780 (2006).
abstract |
|
Janda M., Machala Z., Morvová M., Franček V., Lukáč P.: WEB-EEDF: Open Source Software for Modeling the Electron Dynamics, Acta Phys. Slovaca 55, 507-514 (2005).
abstract |
|
Do not hesitate to contact me to obtain any of these publications. |
Data:
|
N2-CO2 mixture Matrixes with fitting coefficients which enable a calculation of the electron mean energy, drift velocity of electrons, mean free path of electrons, collision frequency of electrons with neutrals and selected electron-impact reactions in N2-CO2 mixture as functions of reduced electric field strength (E/N)) and concentration of N2: n2-co2_matrixes.dat, n2-co2_matrixes.ods Read following paper for more information: Janda M., Martišovitš V., Morvová M., Machala Z., Hensel K.: Monte Carlo Simulations of Electron Dynamics in N2/CO2 Mixtures, accepted in Eur. Phys. J. D (2007) Since this paper was not published yet, please contact me to obtain a draft version. |